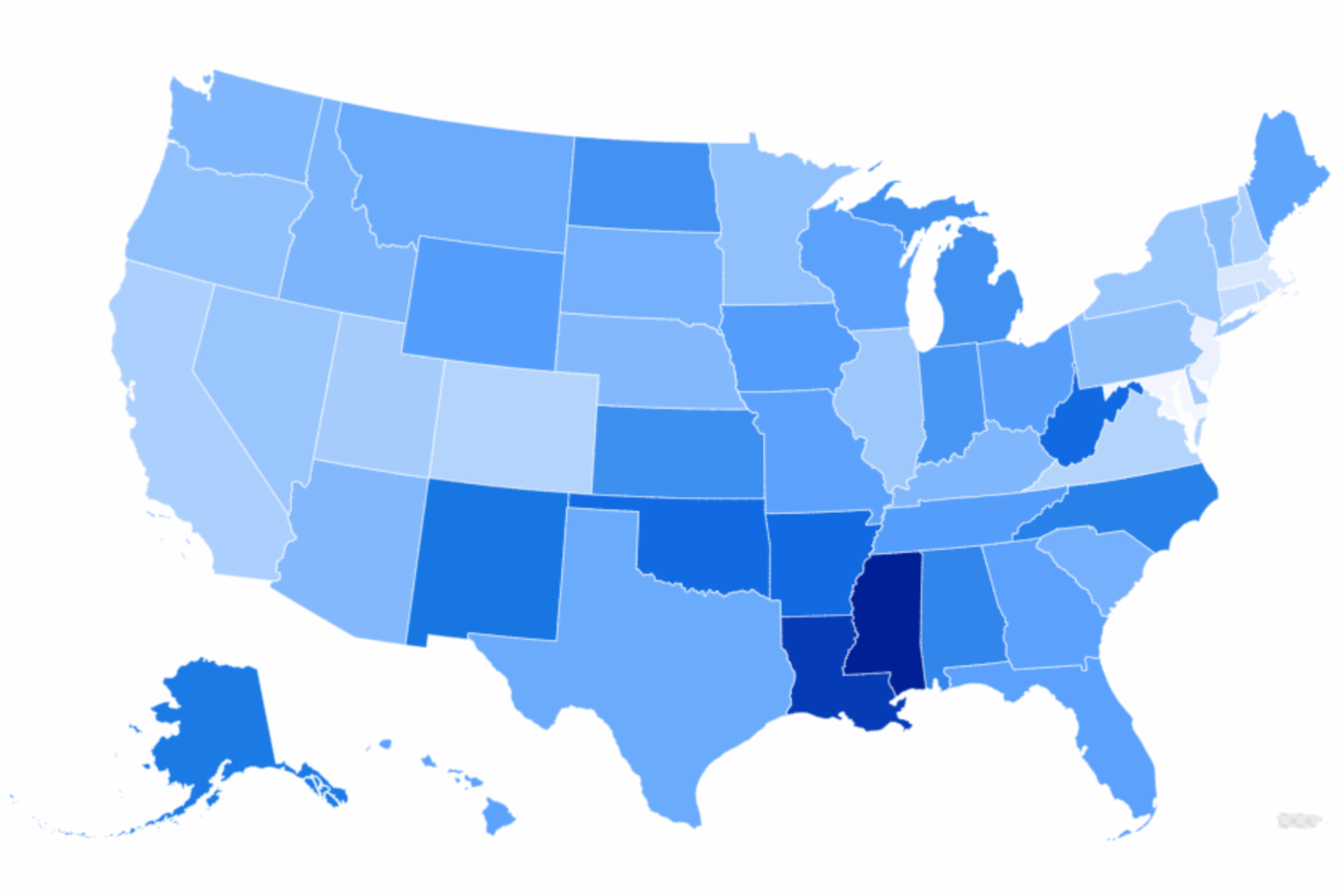
According to recent analysis by WalletHub, residents in five southern states allocate a higher proportion of their household income to healthcare expenses than in other regions across the United States.
The disparities in healthcare costs nationwide are primarily linked to income levels, as the cost of medical services varies significantly from state to state. In states where the median household income is comparatively lower, healthcare expenditures tend to consume a larger share of family budgets, leading to a greater financial burden on residents.
The Significance of Healthcare Affordability
High healthcare costs can impose substantial financial and psychological stress on individuals and families, often resulting in severe consequences such as medical bankruptcy. The potential impact of policy proposals on healthcare affordability underscores the importance of understanding regional disparities.
For instance, recent legislative efforts, including a GOP budget plan that recently cleared the House, threaten to restrict access to Medicaid for over 7 million Americans-particularly affecting populations in Arkansas, Louisiana, West Virginia, and Oklahoma-if enacted into law.
Key Insights into Regional Healthcare Spending
Mississippi leads the nation with the highest percentage of household income dedicated to healthcare, with an average of 18.66%. Following are Louisiana, West Virginia, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, where families typically spend over 16% of their earnings on essential medical services and treatments.
Conversely, Maryland residents experience the lowest healthcare expenditure relative to income, with providers and services accounting for just 9.03% of the median household income in the state.
Mississippi’s median household income stands at approximately $54,915, the lowest in the country, which amplifies the impact of healthcare costs on family budgets. Despite its relatively moderate overall healthcare costs-ranking 38th in the nation for doctor visits-it ranks higher in dental care expenses (12th) and for medications like Lipitor (16th).
Interestingly, the states with the highest share of income spent on healthcare are also among the poorest in the nation, whereas the states with the lowest healthcare expenditure relative to income tend to be among the wealthiest, such as New Jersey, which boasts the highest median household income in the U.S.
Higher wages often correlate with better employer-sponsored health insurance, reduced financial strain from medical bills, and decreased reliance on government programs like Medicaid and Medicare.
The Impact of Medicaid Budget Cuts on Healthcare Costs
The recently approved GOP budget proposes a $700 billion reduction in Medicaid funding over the next decade, coupled with the introduction of work requirements-specifically, a mandate for 80 hours of community engagement per month for Medicaid recipients.
Supporters argue that such work requirements promote employment and self-sufficiency, but critics contend that many Medicaid beneficiaries are already employed in low-wage jobs and that these policies could unfairly penalize vulnerable populations.
Currently, about 20% of Americans are enrolled in Medicaid. Significant cuts could not only affect those directly dependent on the program but also lead to broader increases in healthcare costs for the general population, as uninsured individuals may delay or forego necessary care.
Gerard Anderson, a health policy expert at Johns Hopkins University, explained to Newsweek that losing insurance coverage often results in higher overall healthcare expenses, as uninsured patients tend to seek care in emergency rooms, which is more costly for the system.
He further noted that many Medicaid recipients are already working in low-income, rural areas where job opportunities are scarce, and relocating for employment is often not feasible, complicating the effectiveness of work requirements.
Louisiana Congressman Mike Johnson, whose district faces high healthcare costs and where one-third of residents rely on Medicaid, emphasizes the moral rationale behind these policies, asserting they help young men find employment opportunities.
Public Reactions and Concerns
Health policy experts and advocacy groups have voiced concerns about the potential fallout from Medicaid reductions. Gerard Anderson highlighted that all Americans could face increased healthcare premiums and out-of-pocket expenses as providers pass on higher costs.
Jennifer Wolff, another Johns Hopkins professor, warned that families might be forced to pay more directly or leave the workforce if Medicaid no longer covers long-term care or home-based services.
Meanwhile, House Speaker Mike Johnson defended the work requirements, framing them as a moral obligation to encourage employment among Medicaid recipients, asserting that refusal to work constitutes system abuse.
Next Steps and Legislative Outlook
The proposed budget now moves to the Senate for review. If approved and signed into law by President Donald Trump, it could lead to increased healthcare costs nationwide and significantly impact millions of Medicaid beneficiaries, especially in states with high poverty rates and limited job opportunities.